What's Below in Issue #60:
📰 - A look into stock and option-based compensation
📊 - Data behind the usage of types of stock and option compensation
🎙️ - Podcast w/ Nami Baral
💵- Premium startup resources
🆓- Free startup resources
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Have revenue and need access to quick capital?
The cost of equity capital is getting expensive; debt or working capital might be a better option if you're already generating revenue, and it's non-dilutive.
We've made it easier than ever to get matched with private capital providers and receive offers in minutes, not weeks or months.
*We don't charge any fees to source your debt*
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
How Much Monopoly Money Should I Pay?
One thing that early-stage startups never have enough of is money. The problem is that everything costs money including talent. But how do you pay your employees when you have little or no revenue? The answer is simple: you pay them with monopoly money. Well, not exactly, but close enough.
Stock and option-based compensation is a way of rewarding your employees with a share of your company’s future value. Instead of paying them cash, you give them equity, which is a legal claim to a portion of your company’s ownership. While your company may not be worth much today and the stock feels like monopoly money, the value can become magnitudes larger than any salary would ever pay.
Quick Recap: Stock vs Options
- Stock is a direct ownership of a company. When you give your employees stock, you are giving them actual shares of your company that they can sell or keep as they wish.
- Options are a right to buy stock at a predetermined price in the future. When you give your employees options, you are allowing them to buy shares of your company at a discounted price later.
It is important to remember that neither stock nor options guarantee any form of compensation. They just certify your cut of the profits if the company succeeds. If the company closes, then the stock and options are worthless.
Why Use Stock and Option Based Compensation?
- It helps you conserve cash. Equity doesn’t cost the company anything (other than dilution) but can be worth much more than the salary if the company grows. It lets you be “frugal” and use your limited money for growth.
- It aligns with incentives. By giving your employees a stake in your company, you are motivating them to work harder. Equity creates a sense of ownership and loyalty among your team and encourages them to stay with you for the long term. Additionally, for successful startups, the stock compensation is often worth magnitudes more than any salary that could be offered. Many early Unicorn employees became millionaires with just their stock-based compensation.
- It attracts talent. As a startup, you are competing with established companies and other startups for the best talent in the market. By offering equity, you can differentiate yourself from the crowd and appeal to the most ambitious and talented people who are looking for more than just a paycheck, but also a chance to make an impact and be part of something big.
- Pay Advisors. Everyone can use a mentor – including startups. We usually call them advisors and they also want to be incentivized for helping. Options are a great way to give them a reason to keep giving you feedback and ideas.
Tips for Organizing Compensation
There is no one-size-fits-all formula for determining how much equity to give to your employees. It depends on various factors, such as the stage of your company, the role and seniority of the employee, the market rate, and the negotiation process. However, here are some general guidelines to help you get started:
- Use a cap table. A cap table is a spreadsheet that shows the ownership structure of your company, including the number and percentage of shares owned by each founder, investor, and employee. A cap table helps you keep track of your equity distribution and dilution and avoid any confusion or conflict later on. You can use online tools, such as Carta, Capshare, or EquityBee, to create and manage your cap table.
- Use a vesting schedule. A vesting schedule is a timeline that specifies when and how your employees can exercise their options or sell their stock. A vesting schedule protects you from losing equity to employees who leave your company early or underperform. A typical vesting schedule is four years, with a one-year cliff and monthly vesting thereafter. This means that your employees have to work for at least one year before they can access any of their equity, and then they can access a portion of it every month for the next three years.
- Set up your Employee Stock Option Plan (ESOP). This is part of your cap table that is put aside for giving employees stock. It is important to do this before hiring to ensure that you don’t have conflicts about how people are diluted later on.
Most Common Forms of Options
There are many ways of giving stock and options. However, the most common forms are:
- Incentive Stock Options (ISOs): ISOs are a type of option that offers tax benefits to the employee. ISOs are not taxed when they are granted or exercised, but only when the shares are sold. The profit on ISOs is taxed at the lower capital gains rate, not the higher ordinary income rate. However, ISOs have stricter rules and limitations than NSOs, such as a $100,000 annual limit and a minimum holding period of one year after exercise and two years after the grant.
- Non-Qualified Stock Options (NSOs): NSOs are a type of option that does not offer any tax benefits to the employee. NSOs are taxed as ordinary income when they are exercised, based on the difference between the exercise price and the fair market value of the stock at that time. The profit on NSOs is also taxed as ordinary income when the shares are sold. NSOs are more flexible and common than ISOs, as they can be granted to anyone and have fewer restrictions.
- Restricted Stock Units (RSUs): RSUs are a promise to give stock to the employee in the future, subject to certain conditions. When you give your employees RSUs, you are not giving them actual shares of your company, but rather a commitment to do so when they meet certain vesting requirements, such as staying with the company for a certain period or achieving certain performance goals. RSUs are taxed as ordinary income when they vest, based on the fair market value of the stock at that time.
Relevant Articles for Stock and Option-based Based Compensation
- Startup stock options- 👉 Cake Equity
- What are stock options and how do they work? - 👉 Carta
- How Employee Stock Options Work In Startup Companies - 👉 Forbes
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Data Corner
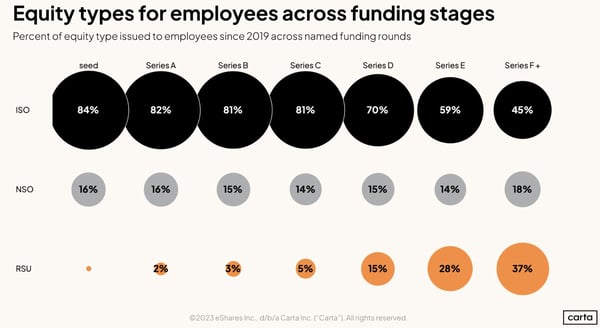
Most Common Equity Compensation By Stage
Options are most common at early-stage companies, while stock becomes more popular at later stages. There is no right way to compensate employees, but knowing industry standards is helpful when attracting talent.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Fundraising Demystified Episode #28 is Live!

Nami Baral shares her journey from the inner workings of Twitter, to founding Niural. The episode unfolds the drama at Twitter that fueled her decision to chart a new path, exploring the nuances of fundraising, from a million-dollar pre-seed round to a $7 million investment for Niural.
Whether you're a startup rookie or a seasoned pro, Nami's insights on dealing with investors, differentiating investment rounds, and building an enterprise-focused product serve as a gold mine. Tune in to gain invaluable perspectives on the challenges, triumphs, and tough decisions in the startup funding world.
In this episode, we talk about:
- Fundraising hacks and lessons, from rookie mistakes to that sweet $7 million raise
- Scaling the business versus selling
- Product design and market transition
Nami Baral is the genius behind Niural, a game-changer in payroll, contractor management, and Employer of Record services across 150+ countries. She's no stranger to startups, kicking off her journey in a company that later teamed up with Twitter, witnessing the rollercoaster of a startup getting acquired and Twitter going public.
Before Niural, Nami founded Harvest, a fintech company that leveraged AI to reduce debt for American consumers. Now, as Niural's CEO, Nami's on her third startup, reshaping the tech scene and making waves in global employment infrastructure. Listen Here
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Free Fundraising Resources
🤓 - Free pitch deck reviews - Submit your deck
💸 - Access working capital fast - Explore options for free
😍 - Free list of AI Recommended VCs - Apply for free
👨💻 - Free fundraising coaching session - Schedule 15 minutes with us
Premium Resources
Your pitch deck built by VCs and designers
🗓️ - Book a one-hour private capital strategy call - Book Now
💫 - Pitch deck design services for founders by VCs - Decko
💼 - Startup Legal Services - Bowery Legal
📚 - Startup Friendly Accounting Services - Chelsea Capital
Upgrade to Thunder Premium to Unlock:
-
Access to VC firms' team tabs to see active partners of the fund & their LinkedIn
-
Navigate a VC's portfolio to see relevant portcos or competitors, quickly find their founders on LinkedIn to connect with them, and request warm introsA downloadable CSV with the investor emails & LinkedIn URLs
-
Ability to filter your matches and adjust your profile
-
LiteCRM to track your progress
-
Request intros to VCs directly through the platform
-
Get our fundraising guide on how to increase your odds of getting a meeting
- Upgrade to lifetime access (one-time fee of $497) and get a free coaching session
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Let's stay in touch:
Written by Jason Kirby - https://www.linkedin.com/in/jasonrkirby
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter for market and industry news and tips when it comes to raising capital and growing your business - https://join.thunder.vc
Seeking to raise capital? Get your list of target VCs by creating a free profile here - https://web.thunder.vc
Looking to raise debt? Explore tailored debt options for free by completing a profile at https://debt.thunder.vc